Generally speaking, the flame retardant grade is determined based on the flame retardant performance of the material under specific conditions. For plastic materials, such as PVC, the flame retardant rating is usually evaluated according to international standards (such as UL 94), which take into account the performance of the material in terms of flame contact, flame spread and dripping. The flame retardant rating of wires is usually determined based on specific industry standards (such as UL 1581). These standards may pay more attention to the performance of the material in electrical equipment, such as heat resistance and arc resistance.
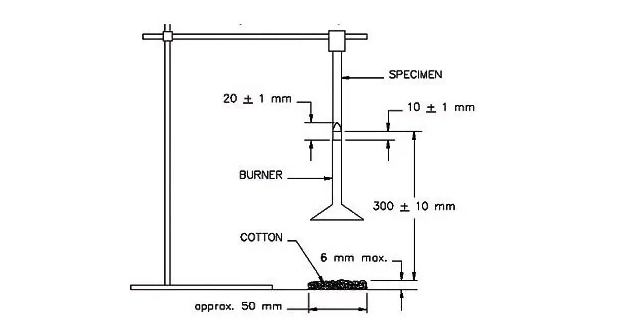
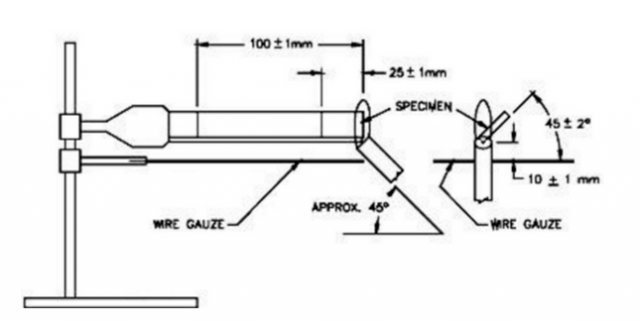 2. Vertical burning test method for materials classified as UL94V-0 ULV-1 ULV-2.
2. Vertical burning test method for materials classified as UL94V-0 ULV-1 ULV-2.
What is UL94?
Flammability UL94 rating is the most widely used flammability performance standard for plastic materials. It is used to evaluate the ability of a material to extinguish after being ignited. There are many evaluation methods based on burning speed, burning time, anti-drip ability and whether the dripping beads burn. Many values can be obtained for each material being tested based on color or thickness. When selecting a material for a product, its UL rating should meet the thickness requirements of the wall portion of the plastic part. The UL rating should be reported together with the thickness value, reporting the UL rating without thickness is not sufficient. The plastic flame retardancy ratings increase progressively from HB, V-2, V-1, V-0, 5VB, to 5VA: HB: The lowest flame retardancy rating according to UL94 standard. Requires the burning speed to be less than 40 millimeters per minute for samples with thicknesses of 3 to 13 millimeters, or less than 70 millimeters per minute for samples thinner than 3 millimeters, or extinguishing before reaching a 100-millimeter mark. V-2: After two 10-second burning tests, the afterflame and afterglow must extinguish within 60 seconds. Droplets from the burning sample can ignite cotton. V-1: After two 10-second burning tests, the afterflame and afterglow must extinguish within 60 seconds. Droplets from the burning sample cannot ignite cotton. V-0: After two 10-second burning tests, the afterflame and afterglow must extinguish within 30 seconds. Droplets from the burning sample cannot ignite cotton. 5VB: After five 5-second burning tests, the afterflame and afterglow must extinguish within 60 seconds. Droplets from the burning sample cannot ignite cotton. Block-shaped samples are allowed to be penetrated by the flame. 5VA: After five 5-second burning tests, the afterflame and afterglow must extinguish within 30 seconds. Droplets from the burning sample cannot ignite cotton. Block-shaped samples are not allowed to be penetrated by the flame.Test Methods
UL94 commonly used flammability tests include the following two test methods: 1. Horizontal combustion measurement method for materials classified as UL94HB. 2. Vertical burning test method for materials classified as UL94V-0 ULV-1 ULV-2.
2. Vertical burning test method for materials classified as UL94V-0 ULV-1 ULV-2.
